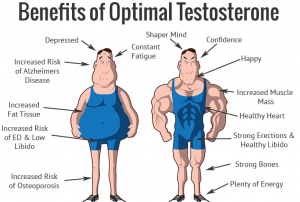
The most common testosterone-related problem in men is hypogonadism, also called low testosterone. Your testosterone level may be abnormally low if you have one or more of the these symptoms: Decreased sex drive;
inability to achieve an erection (erectile dysfunction);Inability to conceive a child; Overall tiredness, etc.
Women with too much testosterone may grow facial hair, develop a deeper voice, or experience decreased breast size. Too much testosterone in women can also cause acne. Too much testosterone in women can be the result of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which can make it difficult to get pregnant and interfere with menstruation.
Abnormally high or low levels of testosterone in men and women can indicate other serious conditions. High testosterone levels can indicate ovarian or testicular cancer. Low testosterone levels can indicate chronic illness or a problem with the pituitary gland, which releases hormones.
In infant boys and girls, signs of abnormal testosterone levels may be more extreme. Testosterone tests are often ordered for boys and girls who aren’t developing properly or when parents notice delayed puberty in either boys and girls.
Boys with low testosterone may grow slowly, with no body hair and poorly developed muscles. Girls with high testosterone may have delayed menstruation or too much body hair. Boys with high testosterone may enter puberty early and robustly.
Sometimes, too much testosterone is the result of a condition known as congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH). This testosterone overload can result in males having an abnormally large penis and females having abnormal genitalia at birth. In some cases, it can cause men to have a very deep voice and women to grow facial hair.
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia can be diagnosed early in infants because it causes dehydration, poor feeding habits, and other symptoms. It can also cause stunted growth, even though someone with this condition may be tall when they’re young.